When comparing analog thermostats to precise PID control, you’ll find that analog devices offer basic, less accurate temperature regulation relying on mechanical parts, which can lead to larger fluctuations and slower responses. In contrast, PID systems use electronic sensors and adjustable parameters to maintain stable, accurate temperatures with high responsiveness. If you want better control for sensitive applications, you’ll discover that PID systems excel—keep exploring to see how they can improve your setup.
Key Takeaways
- Analog thermostats rely on mechanical sensors, offering less precision compared to electronic sensors in PID controllers.
- PID systems provide high control accuracy, maintaining stable temperatures with minimal deviations.
- Analog thermostats respond slowly and often cause temperature fluctuations, while PID adjusts swiftly for better stability.
- PID controllers allow customization of parameters for specific applications, unlike fixed analog systems.
- Overall, PID control ensures smoother, more reliable temperature regulation suitable for sensitive environments.
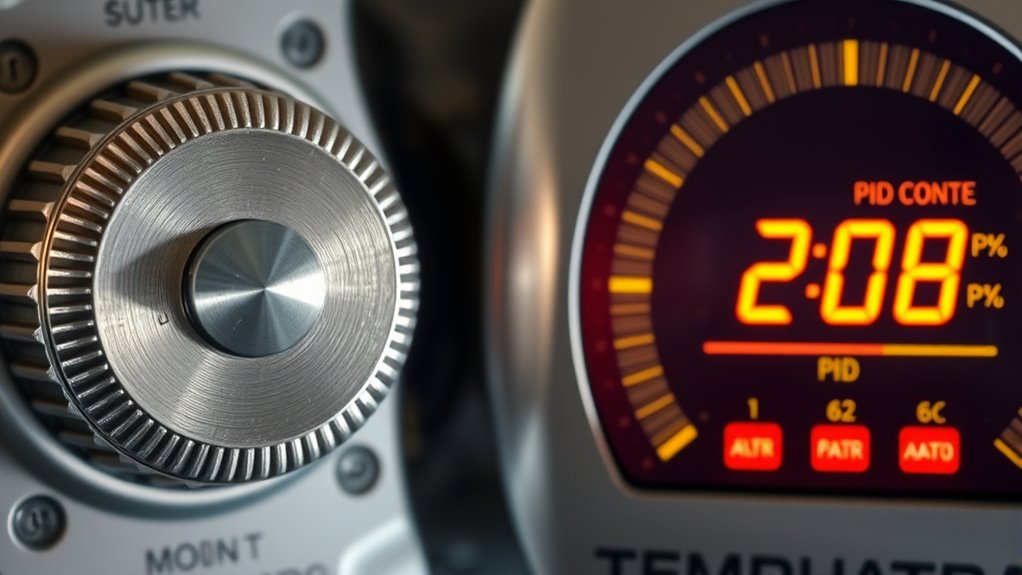
When choosing a temperature control system, understanding the differences between an analog thermostat and a precise PID control is essential. Your decision impacts how accurately and quickly your system responds to temperature changes. An analog thermostat relies on a simple bimetallic strip or mechanical components to sense temperature, which means sensor accuracy can vary depending on factors like calibration and environmental conditions. This often results in a less precise control, especially when maintaining tight temperature tolerances. The system responsiveness of an analog thermostat is generally slower because it reacts only after the temperature drifts outside the set range, leading to larger fluctuations and potential overshoot or undershoot. If you’re managing a process that demands tight temperature stability, these limitations can become apparent quickly.
In contrast, a precise PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control system uses electronic sensors, typically thermocouples or RTDs, which offer higher sensor accuracy. These sensors can detect minute temperature changes with remarkable precision, enabling the PID controller to make real-time adjustments. This high sensor accuracy allows the system to maintain a stable temperature with minimal deviation, which is especially critical in applications like laboratory experiments, industrial processes, or food manufacturing. Because PID control constantly evaluates the difference between the desired setpoint and the actual temperature, it responds swiftly and proportionally to changes, substantially improving system responsiveness. This means your system can adjust output almost immediately, reducing temperature fluctuations and improving overall stability.
Another advantage of a PID system is its ability to fine-tune responses through adjustable parameters, providing a customized approach to control. This flexibility ensures that the system reacts appropriately to different scenarios, whether it’s a rapid temperature change or a slow drift. The responsiveness of a PID-controlled setup minimizes lag time, which is a common issue with analog thermostats, especially in dynamic environments. As a result, you experience smoother, more consistent temperature regulation without the frequent cycling typical of less responsive systems. Additionally, the use of wall organization systems and other stylish solutions in home decor can help create a more efficient environment for temperature-sensitive setups.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Maintenance Costs Compare Between Analog Thermostats and PID Controllers?
You’ll find that maintenance costs are generally lower for analog thermostats because they have fewer complex parts, making them more reliable and easier to troubleshoot. In contrast, PID controllers, while offering precise control, have a higher initial cost and require more frequent reliability analysis and calibration, which can increase ongoing maintenance expenses. Overall, a cost comparison shows analog thermostats are more economical long-term, especially for simpler applications.
Can PID Control Be Integrated With Existing HVAC Systems Easily?
You can typically integrate PID control with your existing HVAC system, but retrofit challenges and compatibility issues may arise. You’ll need compatible sensors and controllers, and sometimes, wiring modifications are necessary. It’s crucial to assess your system’s current setup before installation. While some systems support easy upgrades, others might require more extensive adjustments. Consulting with a professional ensures a smooth integration process, minimizing potential retrofit challenges and compatibility concerns.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Using Analog Versus Digital Controls?
Using digital controls generally reduces environmental impact through improved energy efficiency, which lowers energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. They often use sustainable materials and have longer lifespans, decreasing waste. Analog thermostats might consume more energy due to less precise regulation, leading to higher emissions. By choosing digital controls, you’re supporting material sustainability and contributing to a greener environment through smarter, more efficient temperature management.
Are There Specific Applications Where Analog Thermostats Outperform PID Control?
In humidity control and low energy applications, analog thermostats often outperform PID control. You’ll find them excel in simple, stable environments where precise adjustments aren’t critical, like maintaining basic room temperatures or controlling humidity levels without frequent fluctuation. Their straightforward design means less complexity, lower costs, and reliable operation where exact precision isn’t necessary, making them ideal for settings that prioritize simplicity over sophisticated control.
How Does User Interface Complexity Differ Between Analog and PID Systems?
You’ll find analog thermostats have simpler user interfaces, often just a dial or basic buttons, making for an easy user experience. In contrast, PID systems typically feature more complex interfaces with digital displays, multiple settings, and advanced controls. While this can enhance functionality, it may also require more user effort to understand and operate. Overall, analog systems offer straightforward usability, whereas PID controls provide greater customization at the expense of interface simplicity.
Conclusion
Choosing between an analog thermostat and precise PID control depends on your needs. While analog thermostats are simple and reliable, PID systems offer unmatched accuracy and efficiency. Did you know that PID controllers can reduce energy consumption by up to 20% compared to traditional thermostats? If precision and savings matter to you, investing in PID control could make a significant difference in your comfort and bills. Make your choice based on your specific requirements for ideal results.









